International Automakers Eye Hydrogen FCEV Technology
2013/04/10 | By Quincy LiangClean energy transportation is charting new territory as fuel-cell electric vehicle (FCEV) technology attracts industry attention. The technology got a boost with a series of recent announcements of FCEV alliances among leading automakers, adding critical mass that could help the FCEV market to bloom.
Unlike plug-in electric vehicles (EVs), FCEVs are powered by electricity generated on board in a fuel cell stack through an electrochemical reaction between hydrogen—stored in a purpose-designed, high-pressure tank in the car—and oxygen from the air. The only by-products are water vapor and heat.
Daimler, Ford & Nissan
To accelerate commercialization of FCEV technology, Daimler AG of Germany, Ford Motor Co. of the U.S., and Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. of Japan, recently announced that they have signed a three-way agreement to co-develop a common fuel-cell electric vehicle (FCEV) system to speed up availability of zero-emission technology and significantly reduce investment costs.
The strategy to maximize design commonality, leverage volume and derive efficiencies through economies of scale will help to launch the world's first affordable, mass-market FCEVs as early as 2017, the three partners said.
Together, Daimler, Ford and Nissan have more than 60 years of cumulative experience developing FCEVs. Their FCEVs have logged more than 10 million kilometers in test driving around the world and under a variety of conditions. The partners plan to develop a common fuel cell stack and fuel cell system that can be used by each company to launch differentiated and separately branded FCEVs, which produce no CO2 emissions while driving.
The collaboration sends a clear signal to suppliers, policymakers and the industry to encourage further development of hydrogen refueling stations and other infrastructure necessary to allow the vehicles to be mass-marketed, they stressed.
Powered by electricity generated from hydrogen and oxygen, FCEVs emit only water while driving. FCEVs are considered complementary to today's battery-electric vehicles and will help expand the range of zero-emission transportation options available to consumers.
A senior official of Nissan said that FCEVs are the obvious next step to complement today's battery electric vehicles as the industry embraces more sustainable transportation. "We look forward to a future where we can answer many customer needs by adding FCEVs on top of battery EVs within the zero-emission lineup," he added.
Engineering work on both the fuel cell stack and the fuel cell system will be done jointly by the three companies at several locations around the world. The partners are also studying the joint development of other FCEV components to generate even further synergies.
The unique collaboration across three continents and three companies will help define global specifications and component standards, an important prerequisite for achieving higher economies of scale, they claimed.
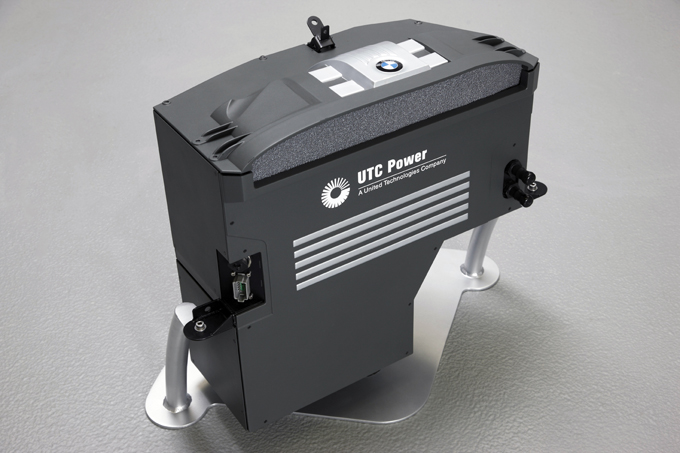

BMW & Toyota
In January 2013, two other leading global automobile conglomerates, BMW of Germany and Toyota of Japan, signed binding agreements to deepen their collaboration.
The two companies claimed that the agreements would help them pursue long-term cooperation on development of a fuel cell system, architecture and components for sports vehicles, and lightweight technologies. These agreements follow a memorandum of understanding signed between the two sides in June 2012.
BMW Group and Toyota also signed a binding agreement to commence collaborative research on lithium-air batteries. The agreement marks the second phase of collaborative research into next-generation lithium-ion battery cells started in March 2012.
According to the two parties, the agreements cover four major areas of cooperation. The first is a fuel-cell system. The companies are convinced that fuel cell technology is one of the solutions necessary to achieve zero emissions. BMW Group and Toyota will share technologies and jointly develop a fundamental fuel-cell vehicle system, including a fuel cell stack and system, hydrogen tank, motor, and battery, aiming for completion in 2020. In addition, the two parties plan to jointly develop codes and standards for the hydrogen infrastructure necessary for popularizing fuel cell vehicles.
The BMW and Toyota cooperation also covers joint development of a sports vehicle.
The companies agreed to conduct a feasibility study to define a joint platform concept for a mid-size sports vehicle to be completed by the end of 2013. The two companies aim to merge their technology and knowledge to maximize customer satisfaction.
Cutting vehicle weight is the third goal of the BMW-Toyota cooperation. The companies plan to jointly develop lightweight technologies for vehicle bodies using cutting-edge materials such as reinforced composites, with an eye to utilize these technologies in cooperation on the joint development of a sports-vehicle platform as well as other BMW and Toyota vehicles.
The fourth cooperation target is to develop a lithium-air battery with energy density greatly exceeding that of current lithium-ion batteries.
Norbert Reithofer, Chairman of the Board of Management of BMW AG said: "Toyota and the BMW Group share the same strategic vision of future sustainable mobility. In light of the technological changes ahead, the entire automotive industry faces tremendous challenges, which we also regard as an opportunity. This collaboration is an important building block in keeping both companies on a successful course in the future."
BMW Group and Toyota first agreed to form a medium-to-long-term collaborative relationship to develop next-generation environment-friendly vehicles and technologies in December 2011. At that time, they also signed a contract under which BMW Group agreed to supply highly efficient diesel engines to Toyota Motor Europe. BMW Group and Toyota have since continued their joint efforts to realize sustainable mobility for the future.
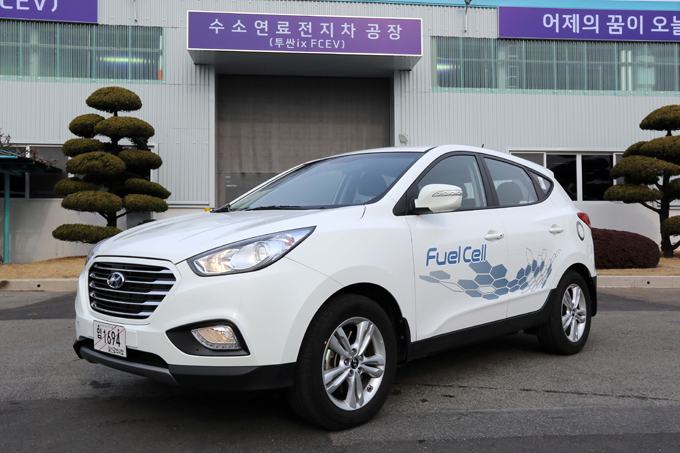

Hyundai
Though it has not disclosed partners in FCEV technology, Korean automaker Hyundai Motor Co., kicked off series production of the ix35 Fuel Cell vehicle at the company's Ulsan manufacturing plant in Korea in January 2013, making Hyundai the first automaker to begin commercial production of a hydrogen-powered vehicle.
A senior official of the company claimed that Hyundai truly believes that hydrogen is the fuel of the future, because it demonstrates the same benefits in terms of range and refueling as an internal combustion-powered vehicle, but emits no harmful emissions, only water.
Hyundai plans to manufacture 1,000 hydrogen-powered ix35 Fuel Cell vehicles by 2015, targeted predominantly at public sector and private fleets, with limited mass production of 10,000 units beyond 2015. Hyundai has already signed contracts to lease the ix35 Fuel Cell to municipal fleets in Denmark and Sweden. Additionally, the EU Fuel Cells and Hydrogen Joint Undertaking (FCH JU) in Brussels has been providing ix35 Fuel Cell vehicles to EU policymakers and the public since October 2011 to demonstrate market readiness of the fuel cell technology.
Hyundai's third-generation fuel cell vehicle, based on the ix35 compact sport utility vehicle (SUV), is equipped with a 100 kW (136 PS) fuel cell stack and two hydrogen storage tanks, with a total capacity of 5.64 kg. This amount of stored hydrogen enables the ix35 Fuel Cell to travel a total of 588 km on a single refuel. Maximum speed is 160 km/h, and it can reliably start in temperatures as low as -25 degrees Celsius. The energy developed is stored in a 24 kW lithium-polymer battery.
In the Name of Hydrogen!
In fact, some aggressive international automakers have been busy in the FCEV segment for some time, including four companies that demonstrated non-commercialized models in the U.K. late last year.
In October 2012, Mercedes-Benz, Honda, Hyundai and Toyota joined forces to demonstrate that hydrogen-powered FCEVs are not just technologies of the future but are here today. The four makers showcased seven FCEV models with hydrogen fuel cells in the U.K. as part of the European Hydrogen Road Tour 2012.
The event aimed to reach out to politicians, industry leaders, media and the public to heighten awareness of FCEVs and their benefits, as well as highlight ways that the U.K. needs to develop in order to accommodate a hydrogen refueling infrastructure. While the technology exists for hydrogen vehicles today, there is a real need to improve hydrogen distribution infrastructure. This tour also marks the most widespread effort to promote FCEVs in Europe to date.
The roadshow moved through Copenhagen, Hamburg, Hannover, Bolzano and Paris, before heading to the U.K. cities of Cardiff, Bristol, Swindon and London, supported by local organizations in each city.
The European Hydrogen Road Tour 2012 is part of the "H2moves Scandinavia" project. The project is the first European Lighthouse Project for hydrogen funded by the FCH JU program. The project focuses on winning customer acceptance for hydrogen-powered FCEVs and preparing the market for hydrogen fuel cell technology. The experience from operating 19 FCEVs in Oslo and Copenhagen and the corresponding hydrogen refueling infrastructure shows that the technology is reliable now, even in harsh Scandinavian winters.